消毒NAVI
鋼製小物
(鑷子や鉗子など)
鋼製小物(鑷子や鉗子など)の消毒方法
鋼製小物の第一選択消毒法は熱水である。
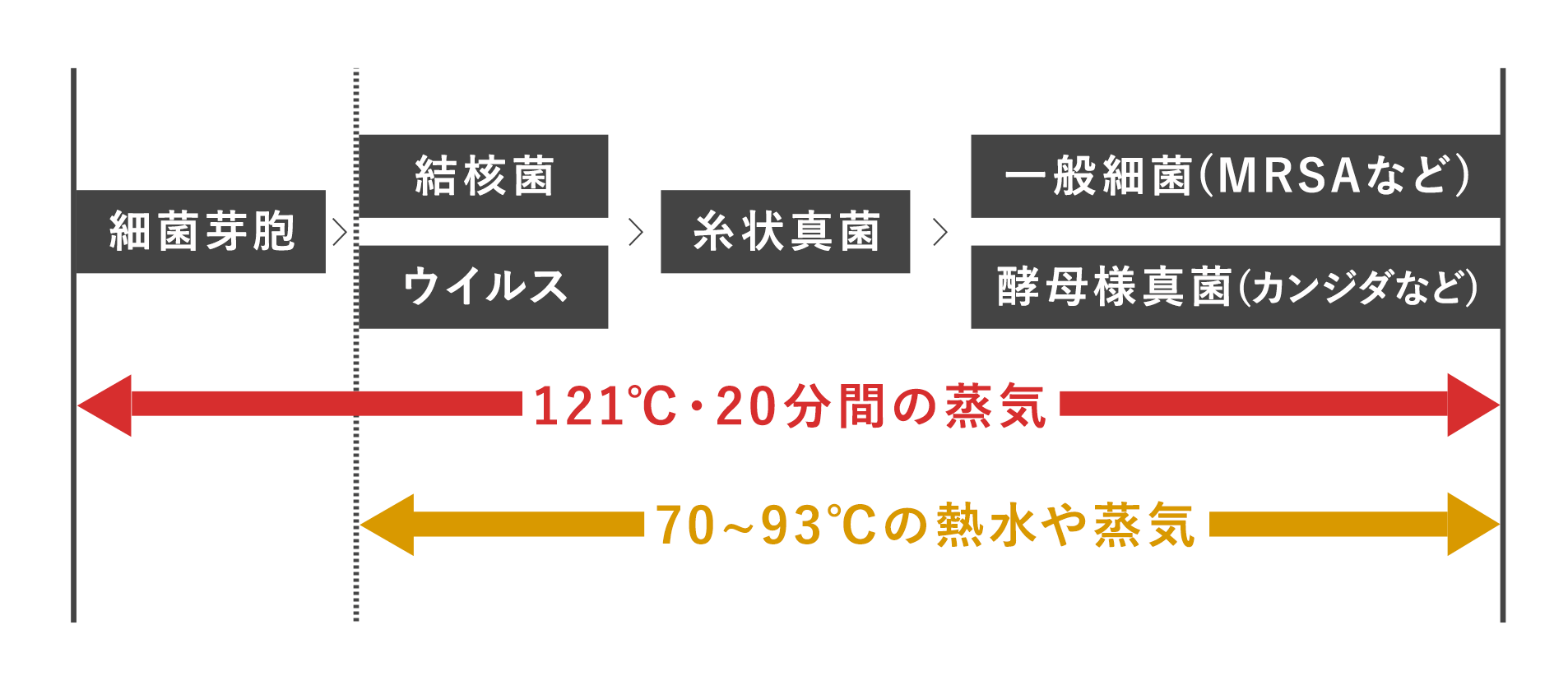
図1に、微生物を熱抵抗性が強い順に並べるとともに、熱(熱水や蒸気)の抗菌スペクトルを示した。
すなわち、70℃以上の熱は芽胞を除くすべての微生物に有効である1-8)。
また熱は、消毒薬に比べて効果が確実で、残留毒性がなく、ランニングコストも安い。
したがって、鋼製小物の消毒には熱が適している。
表1には熱による鑷子や鉗子などの鋼製小物の消毒例を示した。
| 消毒対象 | 利用する装置(条件) |
|---|---|
| 鋼製小物 耐熱性プラスチック器材 |
ウオッシャーディスインフェクタ*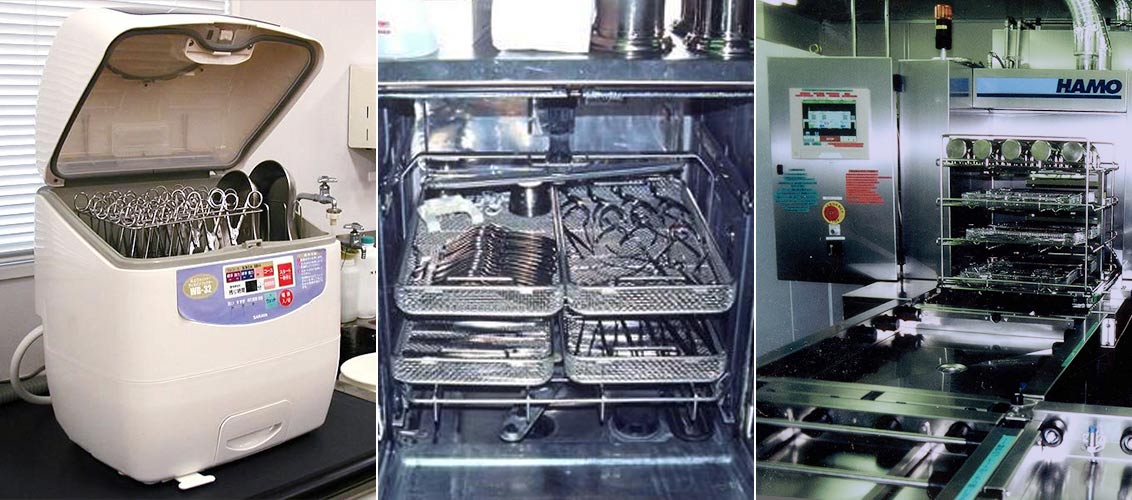 
|
|
家庭用の食器洗浄機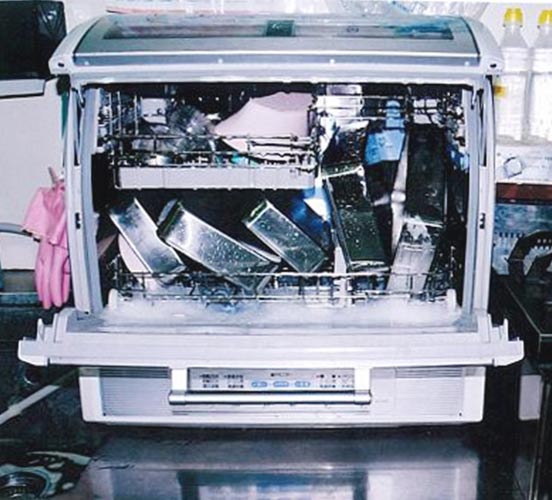  |
- *ウオッシャーディスインフェクタ:「洗浄→熱水消毒」の工程が自動的に行える装置
参考資料
- 1) Barrie D. How hospital line and laundry services are provided. J Hosp Infect. 27: 219-235, 1994.
- 2) Oie S, Kamiya A, Tomita M, et al. Efficacy of disinfectants and heat againstEscherichia coliO157:H7. Microbios. 98: 7-14, 1999.
- 3) Ebner W, Eitel A, Scherrer M, et al. Can household dishwashers be used to disinfect medical equipment? J Hosp Infect. 45: 155-159, 2000.
- 4) Cannon JL, Papafragkou E, Park GW, et al. Surrogates for the study of norovirus stability and inactivation in the environment: a comparison of murine norovirus and feline calicivirus. J Food Prot. 69: 2761-2765, 2006.
- 5) Oie S, Ohkusa T, Kamiya A, et al. Thermal inactivation of spores ofBacillus atrophaeus, Bacillus anthracis, Bacillus cereus, andClostridium difficile. J Hosp Administ. 6: 9-11, 2017.
- 6) Leclercq I, Batéjat C, Burguiere AM, et al. Heat inactivation of the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Influenza Other Respir Viruses. 8: 585-586, 2014.
- 7) Kampf G, Voss A, Scheithauer S. Inactivation of coronaviruses by heat. J Hosp Infect. 105: 348-349, 2020.
- 8) Alizadeh AM, Jazaeri S, Shemshadi B, et al. A review on inactivation methods ofToxoplasma gondiiin foods. Pathog Glob Health. 112: 306-319, 2018.
